ASP.NET MVC でビジネスロジックを実装するのにサービス層を設けたとき、データ検証エラーをコントローラーが持つ ModelStateDictionary へ登録する手段を実装する必要があります。ASP.NET デベロッパー センターのチュートリアル「[C#] #36. フェーズ #4 – アプリケーションの疎結合化」ではDecorator パターンを利用していますが、もっと簡単にできないかなということで、例外通知を利用する方法を考えてみました。サービス層でのデータ検証でエラーとなったときに検証例外を通知し、コントローラー側では検証例外が投げられてきたら、ModelStateDictionary へメッセージを登録するという方法です。
検証用に連絡先一覧のアプリケーションを作ってみました。動作検証の画面は次のとおりです。
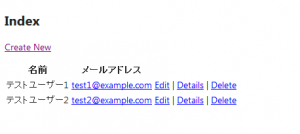
初期状態
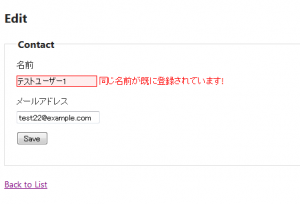
「テストユーザー2」の名前を「テストユーザー1」に変更しようとした画面
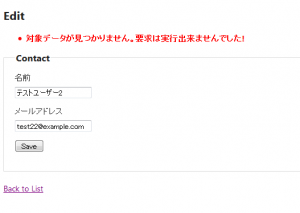
「テストユーザー2」の編集中にデータベース エクスプローラーで「テストユーザー2」のレコードを削除してから更新しようとした画面
それではコードです。
新規作成で ASP.NET MVC 4 Web アプリケーション を選択し、プロジェクト名は「ServiceLayerValidation」とし、テンプレートの選択は「基本」を選んでいます。
まずはモデル。Models フォルダに Contact クラスを作成します。
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace ServiceLayerValidation.Models
{
public class Contact
{
public int Id { get; set; }
[Required]
[Display(Name = "名前")]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Required]
[DataType(DataType.EmailAddress)]
[Display(Name = "メールアドレス")]
public string Email { get; set; }
}
}次に DbContext です。プロジェクトに DAL フォルダを作り、作成した DAL フォルダに ContactsContext クラスを作成します。
using System.Data.Entity;
using ServiceLayerValidation.Models;
namespace ServiceLayerValidation.DAL
{
public class ContactsContext : DbContext
{
public ContactsContext() : base("ContactsDb") { }
public DbSet<Contact> Contacts { get; set; }
}
}次に接続文字列をプロジェクトトップの Web.Config に設定します。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
~省略~
<configuration>
~省略~
<connectionStrings>
<add name="ContactsDb" connectionString="Data Source=|DataDirectory|\ContactsDb.sdf" providerName="System.Data.SqlServerCe.4.0" />
</connectionStrings>
接続文字列の名前は ContactsContext クラスで設定したものになります。
次に動作検証用にアプリケーションの起動毎に DB を初期化するイニシャライザを作っておきます。DAL フォルダに ContactsInitializer クラスを作成します。
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.Entity;
using ServiceLayerValidation.Models;
namespace ServiceLayerValidation.DAL
{
public class ContactsInitializer : DropCreateDatabaseAlways<ContactsContext>
{
protected override void Seed(ContactsContext context)
{
new List<Contact> {
new Contact { Name = "テストユーザー1", Email = "test1@example.com" },
new Contact { Name = "テストユーザー2", Email = "test2@example.com" },
}.ForEach(m => context.Contacts.Add(m));
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
}次にイニシャライザの起動を Global.asax に設定します。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Http;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using System.Web.Optimization;
using System.Web.Routing;
using ServiceLayerValidation.DAL;
namespace ServiceLayerValidation
{
// メモ: IIS6 または IIS7 のクラシック モードの詳細については、
// http://go.microsoft.com/?LinkId=9394801 を参照してください
public class MvcApplication : System.Web.HttpApplication
{
protected void Application_Start()
{
AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas();
WebApiConfig.Register(GlobalConfiguration.Configuration);
FilterConfig.RegisterGlobalFilters(GlobalFilters.Filters);
RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes);
BundleConfig.RegisterBundles(BundleTable.Bundles);
Database.SetInitializer(new ContactsInitializer());
}
}
}次にリポジトリを実装します。DAL フォルダに IContactsRepository インターフェイスを作ります。
using System;
using System.Linq;
using ServiceLayerValidation.Models;
namespace ServiceLayerValidation.DAL
{
public interface IContactsRepository : IDisposable
{
IQueryable<Contact> FindContacts();
Contact GetContact(int id);
Contact AddContact(Contact contact);
void UpdateContact(Contact contact);
void DeleteContact(int id);
void Save();
}
}次に DAL フォルダに ContactsRepository クラスを作ります。
using System;
using System.Linq;
using ServiceLayerValidation.Models;
namespace ServiceLayerValidation.DAL
{
public class ContactsRepository : IContactsRepository
{
private ContactsContext _context;
public ContactsRepository()
{
_context = new ContactsContext();
}
public IQueryable<Contact> FindContacts()
{
return _context.Contacts.AsQueryable();
}
public Contact GetContact(int id)
{
return _context.Contacts.Find(id);
}
public Contact AddContact(Contact contact)
{
return _context.Contacts.Add(contact);
}
public void UpdateContact(Contact contact)
{
_context.Entry(contact).State = System.Data.EntityState.Modified;
}
public void DeleteContact(int id)
{
var target = _context.Contacts.Find(id);
_context.Contacts.Remove(target);
}
public void Save()
{
_context.SaveChanges();
}
#region IDisposable
private bool _disposed = false;
public void Dispose()
{
Dispose(true);
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
}
protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (_disposed) return;
_disposed = true;
if (disposing)
{
// マネージ リソースの解放処理
}
// アンマネージ リソースの解放処理
_context.Dispose();
_context = null;
}
~ContactsRepository()
{
Dispose(false);
}
#endregion
}
}リポジトリでは Dispose パターンを実装しています。詳しい話は「リポジトリパターンを使った際の後始末について」で書いています。
サービス層に行く前にプロパティ名を取得するヘルパーを作ります。プロジェクトに Helpers フォルダを作り、作成した Helpers フォルダに PropertyHelper クラスを作成します。
using System;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
namespace ServiceLayerValidation.Helpers
{
public class PropertyHelper
{
// http://blogs.msdn.com/b/csharpfaq/archive/2010/03/11/how-can-i-get-objects-and-property-values-from-expression-trees.aspx
public static string GetPropertyName<T>(Expression<Func<T>> e)
{
return ((System.Linq.Expressions.MemberExpression)e.Body).Member.Name;
}
}
}次にサービス層です。プロジェクトに Services フォルダを作り、作成した Services フォルダに ITestService インターフェイスを作成します。
using System;
using System.Linq;
using ServiceLayerValidation.Models;
namespace ServiceLayerValidation.Services
{
public interface ITestService : IDisposable
{
IQueryable<Contact> GetListContacts();
Contact GetContact(int id);
void CreateContact(Contact contact);
void EditContact(Contact contact);
void DeleteContact(int id);
}
}次に Services フォルダに ValidateException クラスを作成します。クラスの記述の前に列挙型 ValidationError を記述しています。
この ValidateException クラスが今回の主題です。XML ドキュメント コメントを記述しているので、何をしようとしているのか分かると思います。
using System;
namespace ServiceLayerValidation.Services
{
enum ValidationError
{
DuplicateName = 1,
NotFound,
}
[Serializable]
class ValidateException : Exception
{
private string _targetName;
public ValidateException() : base() { }
/// <summary>
/// 検証エラーとなったプロパティ名とエラーコードを例外で通知します。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="targetName"></param>
/// <param name="errorCode"></param>
public ValidateException(string targetName, ValidationError errorCode)
: base()
{
_targetName = targetName;
base.HResult = (int)errorCode;
}
public ValidateException(string message) : base(message) { }
public ValidateException(string message, Exception inner) : base(message, inner) { }
protected ValidateException(System.Runtime.Serialization.SerializationInfo info,
System.Runtime.Serialization.StreamingContext context) { }
/// <summary>
/// 検証エラーのコードを取得します。
/// </summary>
public ValidationError ErrorCode
{
get { return (ValidationError)base.HResult; }
}
/// <summary>
/// 検証エラーのメッセージを取得します。
/// </summary>
public override string Message
{
get
{
if (base.HResult != 0)
{
return getMessage((ValidationError)base.HResult);
}
return base.Message;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 検証エラーが発生したプロパティ名を取得します。
/// </summary>
public string TargetName
{
get { return _targetName; }
}
private string getMessage(ValidationError errorCode)
{
switch (errorCode)
{
case ValidationError.DuplicateName:
return "同じ名前が既に登録されています!";
case ValidationError.NotFound:
return "対象データが見つかりません。要求は実行出来ませんでした!";
default:
return "不明なエラーが発生しました!";
}
}
}
}次に Services フォルダに TestService クラスを作成します。
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure;
using System.Linq;
using ServiceLayerValidation.DAL;
using ServiceLayerValidation.Models;
using ServiceLayerValidation.Helpers;
namespace ServiceLayerValidation.Services
{
public class TestService : ITestService
{
private IContactsRepository _repository;
public TestService() : this(new ContactsRepository()) { }
public TestService(IContactsRepository repository)
{
_repository = repository;
}
public IQueryable<Contact> GetListContacts()
{
return _repository.FindContacts();
}
public Contact GetContact(int id)
{
return _repository.GetContact(id);
}
public void CreateContact(Contact contact)
{
// 名前の重複の確認
if (_repository.FindContacts().Where(w => w.Name == contact.Name).Count() != 0)
{
throw new ValidateException(PropertyHelper.GetPropertyName(() => contact.Name),
ValidationError.DuplicateName);
}
_repository.AddContact(contact);
_repository.Save();
}
public void EditContact(Contact contact)
{
// 名前の重複の確認
if (_repository.FindContacts().Where(w => w.Name == contact.Name && w.Id != contact.Id).Count() != 0)
{
throw new ValidateException(PropertyHelper.GetPropertyName(() => contact.Name),
ValidationError.DuplicateName);
}
try
{
_repository.UpdateContact(contact);
_repository.Save();
}
catch (DbUpdateConcurrencyException e)
{
if (e.InnerException.GetType() == typeof(OptimisticConcurrencyException))
{ // 同時実行違反例外(この場合はエンティティが削除されている)
throw new ValidateException("", ValidationError.NotFound);
}
throw;
}
}
public void DeleteContact(int id)
{
// 指定された ID のレコードがあるか確認
if (_repository.GetContact(id) == null)
{
return;
}
_repository.DeleteContact(id);
_repository.Save();
}
#region IDisposable
private bool _disposed = false;
public void Dispose()
{
Dispose(true);
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
}
protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (_disposed) return;
_disposed = true;
if (disposing)
{
// マネージ リソースの解放処理
}
// アンマネージ リソースの解放処理
_repository.Dispose();
_repository = null;
}
~TestService()
{
Dispose(false);
}
#endregion
}
}TestService クラスでもリポジトリ同様 Dispose パターンを実装しています。なお。重複チェックは DB 側で行うのが筋だと思いますが、動作検証確認のアプリなのでアプリ側で実装しています。
ちなみに、Entity Framework Code First Migrations の機能を利用して DB 側に UNIQUE 制約を付加する話を「ASP.NET MVC 4 での WebMatrix で提供されているユーザー認証の利用(その3)」で書いたので、興味のある方はご覧ください。
次にコントローラーです。Controllers フォルダに HomeController を作成します。
using System.Web.Mvc;
using ServiceLayerValidation.Models;
using ServiceLayerValidation.Services;
namespace ServiceLayerValidation.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
private ITestService _service;
public HomeController() : this(new TestService()) { }
public HomeController(ITestService service)
{
_service = service;
}
//
// GET: /Home/
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View(_service.GetListContacts());
}
//
// GET: /Home/Details/5
public ActionResult Details(int id = 0)
{
var contact = _service.GetContact(id);
if (contact == null)
{
return HttpNotFound();
}
return View(contact);
}
//
// GET: /Home/Create/
public ActionResult Create()
{
return View();
}
//
// POST: /Home/Create/
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult Create(Contact contact)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
try
{
_service.CreateContact(contact);
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
catch (ValidateException e)
{
ModelState.AddModelError(e.TargetName, e.Message);
}
}
return View(contact);
}
//
// GET: /Home/Edit/5
public ActionResult Edit(int id = 0)
{
var contact = _service.GetContact(id);
if (contact == null)
{
return HttpNotFound();
}
return View(contact);
}
//
// POST: /Home/Edit/5
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult Edit(Contact contact)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
try
{
_service.EditContact(contact);
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
catch (ValidateException e)
{
ModelState.AddModelError(e.TargetName, e.Message);
}
}
return View(contact);
}
//
// GET: /Home/Delete/5
public ActionResult Delete(int id = 0)
{
var contact = _service.GetContact(id);
if (contact == null)
{
return HttpNotFound();
}
return View(contact);
}
//
// POST: /Home/Delete/5
[HttpPost, ActionName("Delete")]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult DeleteConfirmed(int id)
{
try
{
_service.DeleteContact(id);
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
catch
{
return View();
}
}
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
_service.Dispose();
if (_service != null)
{
_service = null;
}
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
}
}Create, Edit, Delete の POST アクションでサービスから投げられてくる ValidateException 例外のハンドリングをしています(例外からプロパティ名とメッセージを取り出して ModelStateDictionary へ登録しているだけですが 😉 )。
次にビューです。ビューは自動生成されたままの状態です 😆
Views/Home/Index.cshtml
@model IEnumerable<ServiceLayerValidation.Models.Contact>
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Index";
}
<h2>Index</h2>
<p>
@Html.ActionLink("Create New", "Create")
</p>
<table>
<tr>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Name)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Email)
</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
@foreach (var item in Model) {
<tr>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Name)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Email)
</td>
<td>
@Html.ActionLink("Edit", "Edit", new { id=item.Id }) |
@Html.ActionLink("Details", "Details", new { id=item.Id }) |
@Html.ActionLink("Delete", "Delete", new { id=item.Id })
</td>
</tr>
}
</table>Views/Home/Details.cshtml
@model ServiceLayerValidation.Models.Contact
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Details";
}
<h2>Details</h2>
<fieldset>
<legend>Contact</legend>
<div class="display-label">
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Name)
</div>
<div class="display-field">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Name)
</div>
<div class="display-label">
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Email)
</div>
<div class="display-field">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Email)
</div>
</fieldset>
<p>
@Html.ActionLink("Edit", "Edit", new { id=Model.Id }) |
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index")
</p>Views/Home/Create.cshtml
@model ServiceLayerValidation.Models.Contact
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Create";
}
<h2>Create</h2>
@using (Html.BeginForm()) {
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
@Html.ValidationSummary(true)
<fieldset>
<legend>Contact</legend>
<div class="editor-label">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Name)
</div>
<div class="editor-field">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Name)
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Name)
</div>
<div class="editor-label">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Email)
</div>
<div class="editor-field">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Email)
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Email)
</div>
<p>
<input type="submit" value="Create" />
</p>
</fieldset>
}
<div>
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index")
</div>
@section Scripts {
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/jqueryval")
}Views/Home/Edit.cshtml
@model ServiceLayerValidation.Models.Contact
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Edit";
}
<h2>Edit</h2>
@using (Html.BeginForm()) {
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
@Html.ValidationSummary(true)
<fieldset>
<legend>Contact</legend>
@Html.HiddenFor(model => model.Id)
<div class="editor-label">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Name)
</div>
<div class="editor-field">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Name)
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Name)
</div>
<div class="editor-label">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Email)
</div>
<div class="editor-field">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Email)
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Email)
</div>
<p>
<input type="submit" value="Save" />
</p>
</fieldset>
}
<div>
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index")
</div>
@section Scripts {
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/jqueryval")
}Views/Home/Delete.cshtml
@model ServiceLayerValidation.Models.Contact
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Delete";
}
<h2>Delete</h2>
<h3>Are you sure you want to delete this?</h3>
<fieldset>
<legend>Contact</legend>
<div class="display-label">
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Name)
</div>
<div class="display-field">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Name)
</div>
<div class="display-label">
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Email)
</div>
<div class="display-field">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Email)
</div>
</fieldset>
@using (Html.BeginForm()) {
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<p>
<input type="submit" value="Delete" /> |
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index")
</p>
}これで動くようになります。
検証エラーメッセージの設定なども強制的に 😛 集約できるので、Decorator パターンよりお手軽かなと思います 😉
「サービス層からの検証エラーの通知」への1件のフィードバック